
Chris Lawrence is a journalist and chief editor at Wlan Labs. He has been writing about technology for more than ten years. He writes about everything ranging from privacy to open source software. His goal is to educate readers about important topics to help make their lives easier.
Phishing has been around since the very early days of the Internet, but as we rely more on the worldwide web, the risks and dangers are becoming more substantial. Recent phishing statistics can reveal a great deal about the true nature of the problem globally.
Phishing itself relates to the practice of sending out fraudulent emails. The emails will often pretend to be from established companies to try and convince their victims that they are a legitimate business and begin building trust with them.
Once that trust has been formed, the cybercriminals behind the fraudulent emails will attempt to gain personal information from their victims, such as credit card details or passwords.
It is important always to be aware of potential threats online, and phishing is certainly no exception.
With this in mind, we are going to be taking a look at fifty phishing stats to help you stay safe and aware when it comes to phishing scams. Let’s get started.
The Rise of Phishing
It is no surprise that today, with our reliance on technology growing more and more prominent daily, phishing attacks are constantly on the rise. We will be looking at some particular stats about this frequency and the rise of phishing attacks.
Let’s take a look:
- IBM published a study showing that one in five companies fell victim to data breaches in 2021, with credentials and information stolen. 17% of these breaches were carried out via phishing.
- Despite this significant increase, only one in five organizations provide phishing awareness training to their employees.
- The 2021 Verizon DBIR report shows that about a quarter of any data breaches involved phishing scams in some way and that a whopping 85% of these breaches, in general, have some kind of human element involved in the process.
- Verizon’s figures are supported by research undertaken by the Internet Crime Complaint Center of the FBI. This research showed that in 2020, there was a record number of complaints filed by Americans that involved a form of phishing.
- The Internet Crime Complaint Center also shows that this was the most significant threat in 2020, with around 241, 342 victims falling prey to phishing. This is more than the victims of other prominent cybercrimes, such as identity theft- which the report showed had a total of 43,330 victims in the United States in 2020-, personal data breaches- with 45,330 victims-, extortion- 76,741 victims-, and non-delivery/non-payment, the second most common cybercrime with 108,869 victims.
- Google Safe Browsing data continues this theory on the rise of phishing, showing that on the Internet there are now almost 75 times more phishing websites than malware websites.
- Research from IronScales suggested a huge increase in email phishing attacks worldwide since March 2020, with their numbers reporting an 81% increase.
- Within the last year, business email compromises- or BEC– had a massive increase of 15% between the second and third business quarters.

The Common Victims of Phishing
Whilst phishing can easily affect anyone; certain victims are targeted more than others.
Businesses, in general, are particularly susceptible, and whilst large businesses are usually the ones that will make the headlines, small and mid-size are often targeted just as much or even more so than larger ones.
This is because these smaller establishments will often not have the kind of security measures that big businesses will have, making them more vulnerable and unable to protect themselves well.
Businesses are not the only organizations that fall prey to these kinds of scams, with sectors such as Education, Finance, and Public Administration also being noteworthy targets of this fraudulent online activity.
Let’s check out some stats regarding the common victims of phishing scams:
- In 2020, research by BDO showed that around six out of ten middle-sized businesses in the United Kingdom fell victims to phishing fraud. These businesses suffered a huge financial strain, with an average loss of around £245,000.
- A fair amount of mid-sized companies and businesses were surveyed regarding this, and a huge 40% of them reported an increase in attempted phishing and online fraud compared to other years.
- Reports of social engineering incidents- as suggested in a report by Verizon- were at the highest in five particular sectors in 2020: Mining and Utilities, Finance, Professional Services, Public Administration, and Education.
- Despite the previous stat, the actual statistics surrounding the most common breaches in certain sectors are slightly different (but only slightly). Public Administration is the most affected sector, followed closely by Mining and Utilities, Professional Services, and Education.
KnowBe4 published a Phishing by Industry report that showed which industries were the most at risk according to their sector and size. In this report, small relates to a business size of one to 249 employees, medium relates to a business of 250 to 999 employees, whilst large relates to a business of more than 1000 employees.
With this in mind, let’s now take a look at some of the stats that this report has to offer:
- A small healthcare and pharmaceutical company has a 44.7% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A small education organization has a 41.1% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A small manufacturing business has a 40.9% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A medium-sized construction business has a 49.7% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A medium-sized healthcare and pharmaceutical company has a 49.2% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A medium-sized general business service organization has a 43.5% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A large technology company has a 55.9% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A large healthcare and pharmaceutical company has a 49.3% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
- A large manufacturing organization has a 46.8% chance of becoming the target of a phishing attack.
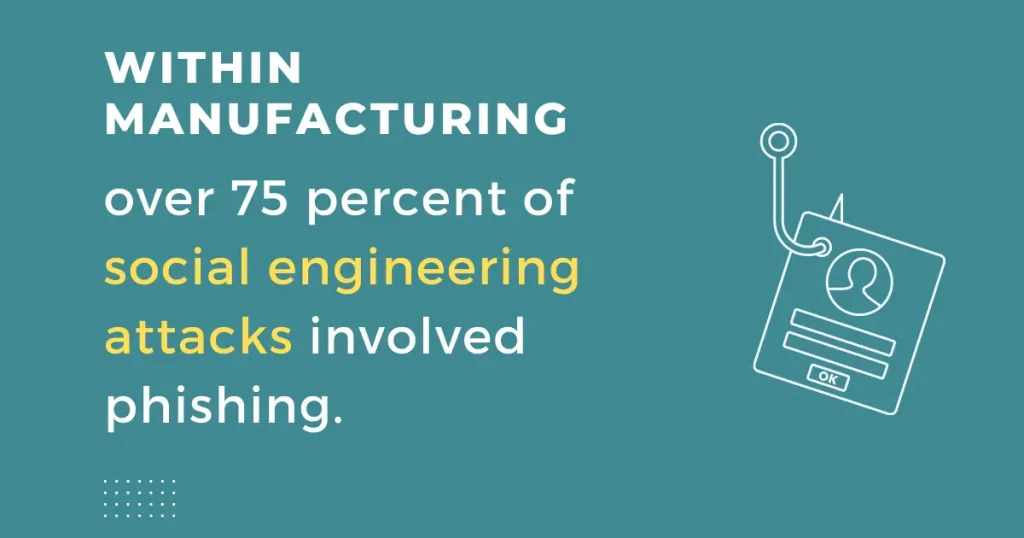
These results show that companies that tend to be targeted more than others are healthcare and manufacturing, along with technology, construction, education, and business services.
This focus on the healthcare sector is also reiterated by a study from IBM, with results that suggested that healthcare is a sector that tends to suffer greatly from phishing attacks, even if the sector isn’t always at the top of the list when it comes to the most breached industries.
How Do People Fall Victim to Phishing?
Due to emails being the common method of phishing attacks (though other methods are becoming increasingly prominent that we will touch on later), one of the most well-known ways people can fall victim to these online scams is via links attached to the phishing emails.
- The 2021 Gone Phishing Tournament results from Terranova Security showed that a surprisingly large number of employees would fall prey to these links and end up clicking on them.
- Even more surprising is that a huge 67.5% of those people will then go on to input their details into the phishing website they are taken to.
- Taking both of these figures into account, Terranova Security suggests that a surprisingly substantial 13.4% of employees across various industries will ultimately input their details into a phishing website.
The Methods of Attracting Victims
It is easy to see that there is certainly something that is attracting victims to phishing scams if the previously mentioned numbers are anything to go by.
But what exactly is it that makes these scams so convincing? Let’s now take a closer look at the ways cybercriminals lure in their victims, as well as some statistics concerning this.
Impersonating Established Brands
One of the most common scam forms which go way beyond just phishing is the impersonation of already established brands.
- Check Point suggests that the most impersonated brand worldwide regarding phishing scams is Microsoft, with 43% of impersonation scams taking on the guise of the popular tech company.
- This is followed by the delivery service DHL- with 18%-, the employment social networking platform LinkedIn- 6%- and the worldwide commerce service Amazon (at 5%).
- A study by INKY also reinforces this, naming Microsoft as the most impersonated brand by scammers, noting that a massive 70% of all brand-related impersonation scams consisted of Microsoft-related phishing emails in 2020 alone.
- INKY also reports that the most common businesses that fall prey to impersonation are technology organizations, which account for 71.8% of impersonation scams. This is followed by the retail, logistics, telecommunications, and finance sectors.
- After Microsoft, INKY reported that other companies frequently used brand impersonation phishing scams, including Amazon, financial service Chase Bank, video conferencing service Zoom, and cloud-based collaborative solution company RingCentral.
Email Subjects
Subject lines in emails are another common method in which scammers can lure in their victims and convince them of their authenticity.
The website KnowBe4 researched the most prevalent email subject lines used in real-life phishing emails.
These were the most common in the third business quarter of 2021, according to KnowBe4:
- Twitter: Your Twitter Account Might Be Compromised
- HR Related: Please Complete This Satisfaction Survey in Regards To Remote Working
- Facebook: Access To Your Facebook Account Has Been Temporarily Disabled As An Identity Check is Needed.
There are also two common IT-related email subject lines:
- Upcoming Changes.
- Strange Activity From Your Email Account.
These subjects suggest that cybercriminals hope to capitalize on two particular areas: the huge influx in online entertainment, social media, and remote working due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- KnowBe4 also reported that 47% of phishing attempts via social media are done via LinkedIn, which is particularly cruel when you consider the struggle to find employment for millions of people during the pandemic.
Threats on The Inside!
It might seem like something straight from a movie, but internal threats are very much a real issue when it comes to phishing scams.
- BDO – an accountancy firm- has researched that whilst half of the reported fraudulence is external, a shocking 34% of businesses have experienced some form of collusion internally between scammers and employees.
- Even more surprising is that many of these businesses have found that the employees caused 21% of these scams.
Email Attachments
Attachments are another highly popular way scammers attract their victims in phishing emails.
ESET compiled a Threat Report of common malicious attachments and files, taking into account the third business quarter of 2021.
The results- from most common to least- were as follows:
- Windows Executables (74%): These files can be run with options or instructions and are found on all operating systems, hence their popularity with scammers.
- Script Files (11%): Text files tend to contain debugger command sequences.
- Microsoft Office Documents (5%): Applications designed by Microsoft, including Microsoft Word for text documents and Microsoft Excel for spreadsheets.
- Compressed Archives (4%): An archive file format that compresses the files.
- PDFs (2%): A printed document style of file format that creates an electronic version of the text, an image, or graphics.
- Java Files (2%): Source code in Java programming language.
- Batch Files (2%): Files with instructions within them.
- Shortcuts (2%): A shortcut link to another file on your computer.
- Android Executables (less than 1%): An executable file intended to work for Android phones.
The Diversification of Phishing Attack Methods
As mentioned, phishing tends to be an email-based cyberattack on both Software-as-a-Service users and webmail users.
This is by far the most common phishing platform, with a study by APWG providing the following figures on the matter:
- 34.7% of all phishing attempts are done via this platform.
- Free webmail providers’ attacks have risen significantly from around 61% to 72%.
Despite the common use of email platforms and services, a study from IronScales.com suggested that cybercriminals are upping their game and branching out by diversifying their phishing methods.
The study asked IT professionals how social engineering attacks had been delivered to them.
Let’s look at the stats from that study:
- 36% delivery via SMS.
- 40% delivery via cloud-based and file-sharing platforms.
- 40% delivery via messaging platforms used by the workforce.
- 44% delivery via platforms used for video conferencing.
This by no means takes away from the fact that phishing is still primarily executed via email. Still, it does mean that people must be even more aware when using any communication platform.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Phishing Scams
We have looked at some stats here that show just how much cybercriminals took advantage of the global pandemic by increasing their phishing efforts significantly.
Let’s look at some stats that reflect this:
- In February and March 2020, when the pandemic began, Barracuda Networks reported an insane 667% spike in phishing emails across businesses
- IBM reported an increase of 11% in BEC attacks in the second quarter of 2020 due to the rise in remote working.
- Abnormal Security reports that from the first quarter of 2020 to the second quarter, the weekly volume of phishing campaigns increased by 389%.
- Complaints were also rife during this time, with IC3 reporting 28,500 complaints of phishing scams related to COVID-19.
- The fear of scams from business owners has certainly grown due to COVID-19, with 76% of these owners admitting to feeling much more vulnerable and exposed to fraudulence since the pandemic began. 66% of these owners still feel concerned about this regarding their business.
- Zscaler reported that between January and March of 2020, there was a gargantuan increase of 30,000% in the number of suspicious messages targeted and blocked by remote workers.
- The New Future of Work report from Microsoft shows the effect on security professionals as well, with 80% of these professionals having to deal with a substantial increase in threats following the move to remote working in many businesses.
- 62% of these professionals stated that these threats involved phishing campaigns.
The Financial Impact of Phishing
It is no secret that these kinds of scams can have a horrible financial impact on the companies in question.
Some of the stats in relation to this impact include the following:
- IBM reports that the average security breach can cost around 4.24 million dollars. Of this cost, 38% of the money is spent on replacing any lost business cost, while 29% is spent on detecting and escalating the breach. IBM goes on to report that the information that is known as the most commonly compromised data is personally identifiable information, which is involved in about 44% of these breaches.
- In 2020, 80% of breached organizations reported the loss of personal customer information.
The Benefits of Training for Security Awareness
Awareness of phishing and other security breaches can be an invaluable asset to employees and has been proven to have a positive impact.
Security awareness training programs are training programs that aim to increase employees’ awareness of information security threats and how to protect themselves from them.
These programs cover email security, social engineering, malware, phishing, and ransomware. They also often include a component that encourages employees to be vigilant about reporting any suspicious activity or potential security incidents.
Security awareness training is an important part of any organization’s overall information security strategy, and it should be updated regularly to reflect the latest threats and best practices.
- A study from Cofense, which focused on analyzing millions of results obtained from simulated phishing campaigns, revealed that 82% of employees with the appropriate training reported the simulated scam within an hour. An impressive 52% reported it within 5 minutes of receiving it, whilst 19% were able to do so within 30 seconds.
- KnowBe4 further this by conducting research on security training, which showed that with one year of completed phishing training, there was an average improvement rate of 87% across a wide range of businesses, industries, and organizations.
The Importance Of Phishing Testing For Employees
Phishing testing is the process of trying to find vulnerabilities in your organization’s security that would allow a phisher to successfully launch a phishing attack against your employees.
This can be done through various methods. These include spear phishing (targeting specific individuals or departments within an organization), email spoofing (sending emails that appear to come from a trusted source but are actually from a malicious attacker), and phone spoofing (making calls that appear to come from a trusted source but are actually from a malicious attacker).
By performing phishing tests, you can identify any weaknesses in your organization and train your team on how to spot them.
Final Thoughts
From the stats we have looked at in this article, it is obvious that there has been and will continue to be a huge increase in phishing emails and scams. This is partly due to the COVID-19 pandemic, alongside the general progression of technology.
There are many ways that a business can protect itself and ensure that its staff maintains a keen eye to avoid any major security breaches.
Security awareness training is one option that- as suggested by the studies and stats above- has an impressive improvement rate when reporting suspicious activity.
Another effective method is keeping track of certain methods that scammers use to lure in their victims- such as certain email subject lines and attachments we discussed earlier.
Hopefully, this article and our list of fifty different phishing-related statistics have helped you on your way to ensuring that you and your employees are always ready to handle suspicious emails and activity and avoid phishing entirely.

