
Chris Lawrence is a journalist and chief editor at Wlan Labs. He has been writing about technology for more than ten years. He writes about everything ranging from privacy to open source software. His goal is to educate readers about important topics to help make their lives easier.
So what is ADFS? Active Directory Federation Service (ADFS) is a Single Sign-On (SSO) solution created by Microsoft.
As a component of Windows Server operating systems, it provides users with authenticated access to applications that are not capable of using Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) through Active Directory (AD).
How Does Active Directory Federation Service ADFS Work?
Active directory federation services (ADFS) is a software component that runs on Windows Server to provide users with single sign-on access to systems and applications across organizational boundaries.
It authenticates users against their home directory and then authorises them to access resources in the federated environment. ADFS supports both identity federation and claims-based authentication.
In the identity federation, a user’s identity is federated across multiple organizations. This allows the user to be authenticated once and access all the resources they are authorized to use in any of the federated organizations.
In claims-based authentication, a user’s identity is represented by a set of claims.
These claims determine whether the user should be allowed access to a particular resource. ADFS can be used to provide single sign-on access to both on-premises and cloud-based resources.
It can also enable cross-organizational collaboration, such as sharing documents or working on projects together.
When users attempt to access a resource that ADFS protects, they are first redirected to the ADFS server. The ADFS server then authenticates the user and establishes whether they are authorized to access the requested resource.
If the user is authorized, they are then redirected back to the resource with a token that contains their claims.
The resource uses the information in the token to determine whether the user should be allowed access. If the user is not authorized, they will receive an error message.
Active Directory Federation Services is a robust and flexible solution for providing single sign-on access to resources located across organizational boundaries.
By authenticating users against their home directory and authorizing them to access resources in the federated environment, ADFS makes it possible for users to have seamless access to all the resources they need regardless of where those resources are located.

What Are The Core Components Of The ADFS System?
The Active Directory Federation Service (ADFS) has four main components: the Federation Server, the Federation Proxy Server, ADFS Web Server and the Web Agent.
- The Federation Server is responsible for authenticating users and issuing security tokens. It can be deployed in a perimeter network, providing an additional security layer.
- The Federation Proxy Server is typically deployed in the DMZ and acts as a gateway between the internal network and the Internet. It forwards requests from clients to the Federation Server and caches frequently requested data.
- ADFS Web Server hosts an ADFS Web Agent, which manages security tokens as well as authentication cookies it sends to enable authentication.
- The Web Agent is responsible for protecting web-based resources. It can be deployed on each web server or load balancer in the environment.
Each of these components plays an important role in providing a secure federation solution. By deploying them in a perimeter network, organizations can provide an added level of security for their data and applications.
How Does ADFS Work In Office 365?
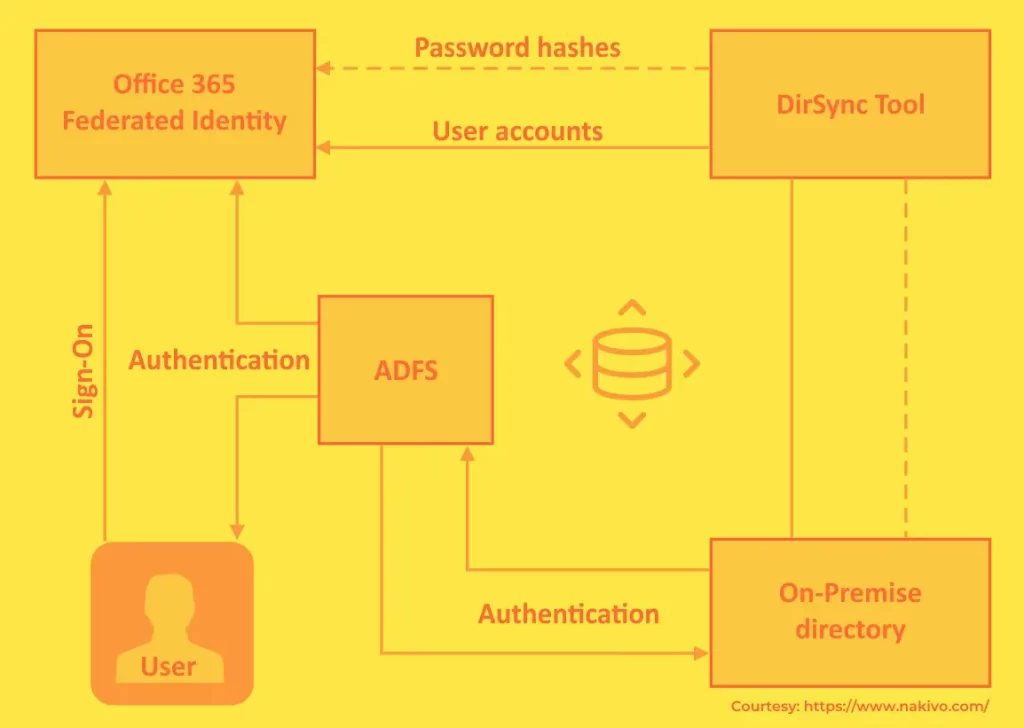
Why Do organizations And Companies Use ADFS?
There are many reasons why organizations use Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS). ADFS allows organizations to extend their Active Directory (AD) authentication capabilities to devices and applications outside their physical network.
This is particularly useful for organizations with remote employees who need to access resources from multiple locations.
In addition to extending authentication capabilities, ADFS also provides a single sign-on (SSO) solution for organizations.
SSO allows users to log in with just one set of credentials, simplifying the process of logging into different applications and systems.
This is particularly useful for organizations with employees who need to access various resources daily.
Overall, ADFS provides several benefits for organizations that need to authenticate users and provide them with access to resources from outside of their network.
By extending AD authentication capabilities and providing a single sign-on solution, ADFS can help organizations to improve their security posture and make it easier for employees to access the resources they need.
What Are The Limiting Factors Of Active Directory Federation Service ADFS?
Although ADFS is a powerful tool for managing access to resources, it does have some limitations:
- First, ADFS requires a high level of expertise to configure and manage. This can make it difficult for organizations to use ADFS effectively without dedicated staff members familiar with the system.
- Additionally, ADFS can be complex to troubleshoot when problems occur. This is because errors can occur at any point in the authentication process, making it difficult to identify the root cause of the issue.
- Finally, ADFS is not designed to work with all applications. In particular, applications that do not support SAML or WS-Federation may not be compatible with ADFS.
As a result, organizations considering using ADFS should evaluate whether the system will meet their needs before deploying it.
What Is ADFS FAQs
What is the difference between AD and ADFS?
AD and ADFS are both Active Directory (AD) technologies. AD is a technology that allows Windows domains to be set up and managed. An AD domain is a collection of computers that are joined together to share resources, including a common security database.
ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services) is an extension to Active Directory that enables the authentication of users from other forests or domains.
When you set up ADFS, you create what is called a federation trust between your organization’s forest and the forest or domain of the users you want to authenticate.
This federation trust establishes a secure connection between the two forests, allowing users in the other forest or domain to be authenticated by your organization’s Active Directory domain controller.
What is federation Active Directory?
Federation Active Directory (FAD) is a term used in the Microsoft Windows Server 2008 operating system to describe the ability to join two or more domains that the same organization does not administer but that trust each other.
Federation Active Directory allows administrators to extend their Active Directory infrastructure across organizational boundaries by configuring trusts between domains.
This configuration enables users in one domain to access resources located in another domain without having to authenticate again. Trusts can be established between domains in different forests or domains in the same forest.
How do I check Active Directory Federation Services?
Server Manager can be used to check the status of ADFS. This means that users can sign in to an application with their organizational credentials, and the application will trust the identity provided by ADFS.
A typical use case for ADFS is allowing Single Sign-On (SSO) access to Office 365 from a corporate network.
In this scenario, users would sign in to their computer using their organizational account and then be able to access their Office 365 email without having to enter their credentials again.
What is the difference between LDAP and ADFS?
The primary difference between LDAP and ADFS is that LDAP is used to authenticate users over a network connection. In contrast, ADFS is used to provide Single Sign On (SSO) capabilities for web-based applications.
LDAP uses bind operations to authenticate clients with servers. The LDAP server will ask the client to provide proof of identity through a distinguished name (DN) and password. If the client can successfully produce this information, they are considered authenticated.
ADFS, on the other hand, uses federation technologies such as Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) and WS-Federation to provide SSO capabilities. With ADFS, users are redirected to a login page where they enter their organizational credentials.
These credentials are then used to generate a SAML assertion sent to the ADFS server. The ADFS server uses the assertion to authenticate the user and generate a security token.
This token is then passed to the application, which allows the user to access the resources they are authorized to access.
What is azure ADFS?
Azure ADFS is an identity management service that is hosted on Azure. It provides single sign-on access to cloud and on-premises applications.
It uses industry-standard protocols such as Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0, WS-Federation (WS-Fed) and WS-Trust to provide a claims-based access control model for authenticating users and authorizing access to resources.
Azure ADFS also supports other features such as multi-factor authentication, self-service password reset, etc.
What is ADFS 3.0?
ADFS 3.0 is the third version of Active Directory Federation Services, a software component developed by Microsoft that can be installed on Windows Server to provide Single Sign-On (SSO) and access control capabilities for external web applications and services to an organization’s Active Directory Domain.
Compared to earlier versions, ADFS 3.0 is a major upgrade with new features and enhancements.
The most notable is support for claims-based authentication and authorization, Web Application Proxy integration, automatic Certificate enrollment for domain-joined computers, and support for delegating administration.
Overall, ADFS 3.0 provides a more flexible and extensible platform for implementing federated identity solutions in your environment.
What is ADFS SSO?
ADFS is an acronym for Active Directory Federation Services. It is a tool that allows businesses to provide secure single sign-on (SSO) access to their employees, partners, and customers.
By using ADFS, organizations can simplify the management of user identities and reduce the cost and complexity of maintaining disparate identity stores.
When a user tries to access a resource that is protected by ADFS (such as an email account or an internal website), they are redirected to the ADFS server.
The server then authenticates the user against their on-premises Active Directory store and issues them a security token. This token allows the user to access the requested resource.

