Chris Lawrence is a journalist and chief editor at Wlan Labs. He has been writing about technology for more than ten years. He writes about everything ranging from privacy to open source software. His goal is to educate readers about important topics to help make their lives easier.
If your organization is online, and in the Digital Age, everyone is online, you need multi-factor authentication (MFA). But what is multi factor authentication and does it matter? This is a tool that organizations use to secure their online services to keep the unwanted hackers out and only their employees and clients in.
Chances are that you have already used multi-factor authentication or at least two-factor authentication for an online account of yours; you may just not have realized that’s what you were using. Now it’s time for you to implement it for your own organization.
Want answers to what is multi-factor authentication and how it works? This guide has everything you need to know.
The Basics of Multi-Factor or Two-Factor Authentication
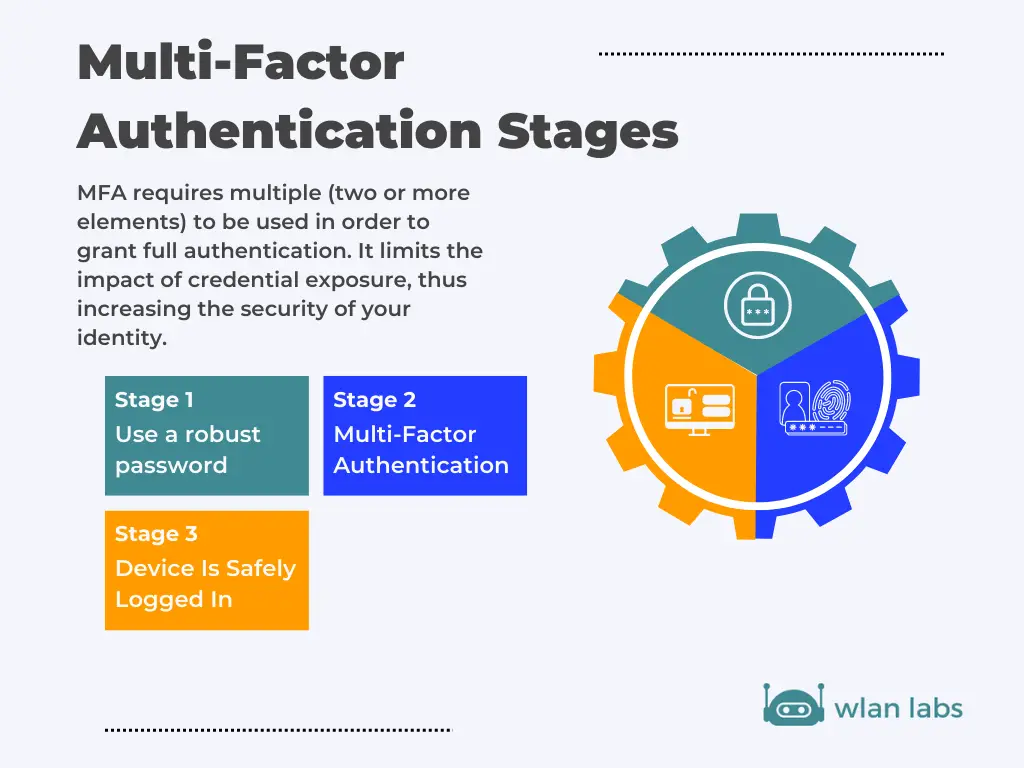
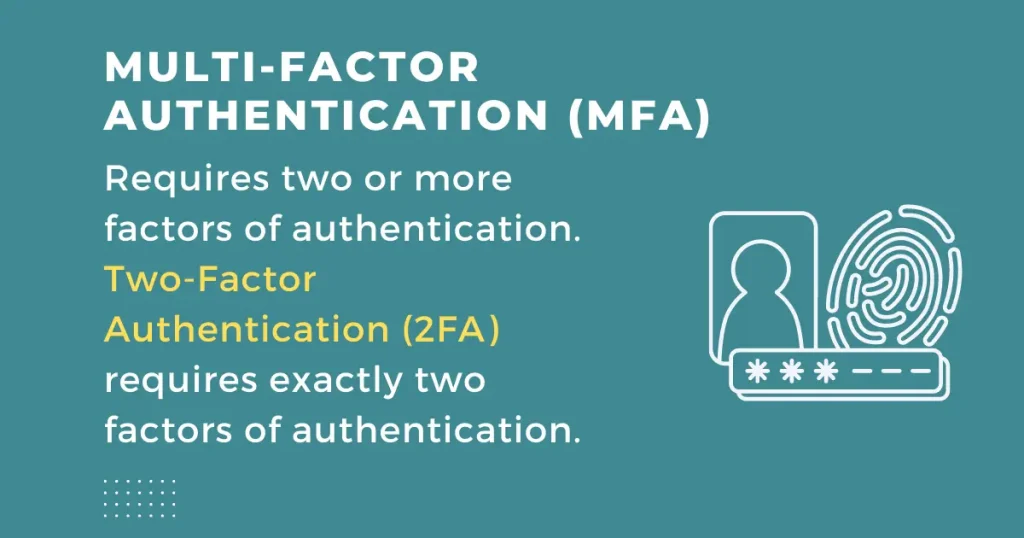
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires two or more factors to be met for a user to gain network access or log in to an account. You may also hear this system referred to as two-factor authentication. As you may imagine, two-factor only requires two factors, whereas other systems may have multiple authentication factors to gain access to a system.
MFA authentication methods vary from a one-time password sent to a mobile device to hardware tokens that act as security keys. But the same principle remains. While any attacker can hack a one-layered security system and guess a password, multi-factor authentication puts more pressure on the user to confirm their identity, better protecting any system.
Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
Cyber security isn’t just a want to have or “that would be nice”. Cyber attacks against businesses are on the rise. The even worse news is that the severity of ransomware attacks, in particular, is trending up. Unauthorized users gaining access to your business applications and network could have severe consequences. You, as a leader, must do everything in your power to prevent phishing, brute force, and social engineering attacks.
The multiple layers of multi-factor or two-factor authentication ensure only people you trust can access your systems. This keeps your company and client data safe from attacks, saving you an embarrassing PR nightmare, loss of client trust, and the money you’d inevitably have to spend to recover from an attack.
How Do You Use Multi-Factor Authentication?
Now you understand the basics, but by what means multi-factor authentication achieves the security you’re looking for for your organization?
Typically, to sign in to an account, a user merely needs to enter a username or email and a password. Multi-factor authentication adds more requirements to prove the user is who they say they are and authorized to gain access. So all a user needs to do is follow the prompts and provide the necessary proof that they are who they claim to be.
The factors you use will vary by the MFA provider you choose. We’ll cover the possible elements in greater detail below.
Multi-Factor Authentication Factors
We’ve mentioned that authentication factors are required for a user to log in when an MFA system is in effect. But what do those factors look like? If someone submits the correct password, what would the second factor be to confirm a user’s identity verification?
When an MFA system is designed, each layer must come from one of these factors. A combination of different factor types must be used for the protection to be effective. These are the types:
Knowledge-Based Authentication. This is all about what a user knows. The knowledge factor may include security questions, passwords, or PINs. This factor is the most easily revealed by hackers and the weakest security factor — though also the most common.
Possession Factor Authentication. A possession factor is something a user has, such as a hardware token to use as a key like a USB, software tokens that may be found on smartphone apps, or one-time codes or passwords sent to a mobile device.
Biometric Authentication. This may also be referred to as an inherent factor because it’s something inherent to a user that can’t be duplicated. Tools like facial recognition, voice recognition, or fingerprints fall under this category.

Additional Factors for Strengthening MFA Security
Systems will vary on what they require of each user. Perhaps it’s one of each factor, or there may be duplicate factors by different means. The top MFA systems also include risk-based authentication to determine how many layers should be added for a login session.
This factor studies behavioral biometrics to determine if there is abnormal activity. You may have seen risk-based authentication via a Google authenticator. For example, if you log in from a new device, it will prompt additional MFA credentials that you wouldn’t usually need to complete.
Additionally, while the above are the core three factors (knowledge, possession, and biometrics), physical location is now being adapted as a fourth factor. If a user isn’t logging in from a suspicious location reported by their GPS on a mobile phone, this is a red flag.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication Good For?
In two-factor and multi-factor authentication systems, the system requires that different factors are used to authenticate a user’s identity.
So, for example, a system with a password requirement and security questions wouldn’t count as multi-factor authentication because they’re both knowledge factors. But if security questions are combined with physical tokens, for example, this would be a knowledge factor and possession factor.
This means that MFA is best for preventing three types of attacks:
- Phishing Attacks. These attacks involve a hacker tricking a user into revealing information, and users are particularly susceptible to these attacks. But even if a hacker gains the knowledge necessary to log in, they won’t have the hardware token or biometric data required, keeping your system safe.
- Social Engineering. Phishing falls under the social engineering umbrella, but there’s much more to social engineering than the most common form of attack, phishing. All of these involve manipulating a user. But just as with phishing, the user can’t possibly reveal everything required for the login process.
- Brute Force. Rather than tricking a user or stealing information, this attack means a hacker submits passwords repeatedly to guess the correct one. This may seem primitive and unworthy of concern, but this form of attack is both popular and effective.
What is Multi-factor Authentication Video Explanation
Who Should Use Multi-Factor Authentication?
Everything is online now, from basic task management software to private, sensitive client data. And while you may not imagine that there are hackers after your organization’s data and say, “We’re just a small business. Hackers are after big financial institutions and businesses like Apple or Google,” you’re wrong. In fact, small businesses are more frequent targets of cyberattacks than larger companies.
While every organization should use at minimum two-factor authentication to protect its data, this is especially important if you offer online services to clients.
While you can train your employees to avoid phishing scams, stick to trustworthy networks, and use tough security questions, users are largely beyond your control. But allowing access to your system through a user’s account is still dangerous. MFA on both the employee and client-side of your system ensures everything possibly entry is airtight.
The Benefits of Multifactor Authentication
Not convinced about the power of multi-factor authentication?
Here are the benefits you need to know before you stick to only using strong passwords:
Better Security
Just as you wouldn’t leave a bank unlocked and unguarded, you must protect your data from social engineering, phishing, and brute force attacks. Physical tokens like security keys and multi-factor authentication credentials will keep your system safe.
Supports Remote Workers
Many traditional security measures for businesses are on-site solutions. But how do you continue working productively and keeping things secure when employees are off-site? MFA can work from anywhere and ensure that only authorized personnel are logging on, even if they’re nowhere near the office.
Boost Your Credibility
As tools like Google authenticator become more commonplace, users expect organizations to do everything in their power to avoid data breaches. So while you may imagine users will be annoyed by the extra steps, most will genuinely appreciate the added security, lending more respect and credibility to your business.
Avoid the Costs of Recovering from Cybersecurity Threats
Cloud computing is only growing in popularity, meaning that more sensitive information is available remotely. If you’re attacked, the costs associated can be severe. You might have to pay a ransom, you’ll have to invest in rebuilding your security, and you may lose customers who no longer trust you. Avoid all these money pits by keeping things secure before an attack.
Avoid Password Problems to Confirm User’s Identity
If your organization requires a strong password but a user can’t ever remember it, you could be devoting more support desk time to helping them log in. But if users can regularly use a one-time password that they don’t have to remember and supply inherent or knowledge-based information, no more troubleshooting forgotten passwords.
The Drawbacks of Multifactor Authentication
While MFA is recommended for any organization’s business applications and network access restrictions, that doesn’t make it a flawless setup.
Here are a few drawbacks to consider before installing these security measures:
A Physical Token May Be Lost
If the entire authentication system hinges on tokens, be prepared for some hiccups. Physical security tokens can be misplaced, unlike facial recognition, which ensures you’ll never be without your way in. While these are ideal for avoiding attacks, ensure there is a backup for when an employee absolutely needs to log on but doesn’t have their necessary USB or fob.
Phones Needed to Get a Code
Randomly generated verification codes sent to a user’s mobile device are one of the most popular forms of user authentication method via possession. However, many users may not always have their mobile phone readily available or may not be able to receive an SMS verification.
When this happens, you’ll need to have a customer-friendly backup method to ensure excellent customer support without compromising your security.
The Systems Can Be Expensive
Various MFA solutions come with different price tags. So while there are budget-friendly options available, you may have trouble finding the ideal system if your business is strapped for cash.
However, keep in mind that data and account security should be a top priority for your business. If you can’t keep your client’s data safe, you don’t deserve to have it. In fact, government regulations may be coming and working to increase the liability of businesses that are victims of a data breach if they didn’t have the proper security measures in place before the attack.
So while furthering your cybersecurity may not necessarily be where you want to put your budget, proper protection is crucial for running your business. And remember to look for affordable options before agreeing to the most expensive plans.
Security Isn’t Absolute
It’s true — MFA won’t keep every hacker out. If determined, there are ways a dedicated hacker can bypass MFA protections. However, a security system reliant on username and password alone is far more vulnerable and simply isn’t enough.
So while you still must invest in additional security to keep hackers out, and a highly sophisticated attack may still get through, you shouldn’t be caught without MFA protections.
It Takes Time to Set Up
If you’re using certain services, it’s quick and easy to opt into their authentication systems. For example, organizations using Microsoft products can use the Microsoft authenticator to protect their accounts.
However, suppose you’re looking to install an on-premises, organization-wide authentication set up to protect all your systems, networks, and accounts. In that case, this will take time and will be best performed by experts. Don’t expect to decide today that you want a large-scale system in place and expect it to be done by tomorrow.
So while this will take time, there’s also a lesson in this: the best time to get started on increasing security is now. Hackers don’t wait until you’re ready before they strike. So if you don’t already have a security system in place that you trust, it’s now time to get started.
Is Multi-Factor Authentication Effective?
If you’re still on the fence about whether MFA is worth the time and money to install, know that this security protection is nearly 100% effective. Without multiple kinds of factors required for login, it’s far too easy for hackers to breach your system. But it’s very rare for a hacker to be able to use simple guesses or tricks to gain access if some combination of knowledge, possession, and biometric data is re required.
What makes this protection even more effective is the use of adaptive MFA. With this feature, even a clever hacker can be identified by the system and forced to offer further credentials, which they usually cannot.
How Hackers Get Around These Measures
But does MFA work to completely secure your business 100% from any type of attack without the support of other security measures? No.
First, it’s essential to acknowledge that there are forms of cyberattacks beyond what MFA is designed to prevent.
These forms of attacks include:
- BEC attacks (business email compromise).
- Spoofed login pages
- Embedded malware
- CEO fraud
In addition to these attacks, there are times that hackers circumvent protections to continue with their attacks, even if they are forms of force or phishing. For example, attackers may trick the wireless carrier into sending texts to the hacker’s number for two-factor authentication.
Most ways hackers bypass security is by tricking users into revealing a verification code or one-time password, which shows the benefit of multi-factor methods over two-factor ones.
Is Multifactor Authentication Better Than a Strong Password?
A strong password is a good way of avoiding a brute force attack as they’re difficult to guess. But it’s not perfect for securing your systems.
For example, if someone uses a strong password that is the same password across platforms, this means if one password is hacked, other accounts will be vulnerable as well. Additionally, a strong password can still be guessed. And if a user is subject to a phishing attack, you will want to have other MFA authentication methods in place.
A security token or possession method like a text message sent to mobile phones will keep the computing device secure. Even better is when risk-based authentication is involved to require further proof if user behavior is suspicious.
So while a strong password should be part of securing a user account, it shouldn’t be the only thing stopping a hacker from breaching your data.
Implementing Multifactor Authentication for Your Organization
As workers go remote and cloud computing is standard, multi-factor or two-factor authentication should be a top priority.
Shopping for MFA for your organization? You might find our best multi factor authentication apps guide to be insightful.
Here are some features we recommend to ensure you’re getting something that’s worth your money:
Adaptive MFA: Adaptive MFA analyzes a user’s behavior (Where are they signing in from? Is this the same device as yesterday?
Are these abnormal hours?) and determine if the activity is suspicious. This risk-based authentication assessment may require more MFA credentials to log in successfully.
- Self-Service: By allowing users to decide which credentials they’ll provide to log in, they can choose the tools they’re most confident in using, limiting the support you’ll need to provide.
- Single Sign-On: If you offer multiple applications, single sign-on allows employees and users alike to log in to your eco-system with one log-in attempt instead of needing to do it for each account separately.
- Simple Management Controls: As an admin, you want to know your system is working and that you can keep it running well. The top providers offer in-depth reports to see that the MFA is doing its job and deleting users as needed.
- Excellent Integration: Beyond the MFA itself, additional factors to keep in mind are how easy it is to set up and that it will integrate well with the applications and systems you already use.
What is ADFS?
ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services) is a Microsoft Windows Server role that provides authentication and authorization support for applications that are accessed externally.
For example, assume you have an application running on a web server in the corporate network. This application is accessible to users on the Internet, but you want to make sure that only authorized users can access it.
You could use ADFS to provide authentication for the application. When a user tries to access the application, he or she would be redirected to the ADFS server, where he or she would be authenticated. If the user is not authorized, he or she would be denied access to the application.
Adding Multifactor Authentication to Your Security System
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) solution should be a core component of your cybersecurity system. This, in conjunction with additional security, is crucial to keeping systems protected from those who would want to harm your organization.
You can choose the best system for your organization, employees, and users. Whether you opt for a two-factor authentication method like SMS tokens or a hardware token or prefer biometric authentication methods as well, multi-factor authentication should be a top security priority for any business that wants to keep its data safe.