
Chris Lawrence is a journalist and chief editor at Wlan Labs. He has been writing about technology for more than ten years. He writes about everything ranging from privacy to open source software. His goal is to educate readers about important topics to help make their lives easier.
One question the team is asked fairly often is what is the difference between phishing and pharming?
Pharming and phishing are two types of cyber theft scams that target internet users. Both involve using fake websites or emails to trick people into entering personal or financial information.
Phishing is the more common of the two, with over 3.5 million reports in 2021 alone. Pharming is less common but can be just as dangerous.
In 2021, pharming and email phishing statistics show that these scams are still a significant problem.
Although phishing scams accounted for the majority of complaints, pharming scams have also increased in recent years.
In 2021, there were over 1,000 reports of pharming schemes, which is a significant increase from previous years. These numbers show that phishing and pharming scams constitute a real problem.
If you receive an email or text message that looks suspicious, do not click on any links or enter personal information. It would help if you also were careful when visiting websites, as some fake websites can look very realistic.
What is Phishing?
Phishing in cyber security is one form of social engineering in which cyber thieves transmit a false message to trick the victim into divulging sensitive data such as bank account numbers to an attacker or to inflict malware that is malicious to the victim’s network, such as ransomware.
Phishing attacks can be tough to detect because they often use spoofed email addresses and websites that look legitimate. Email phishing attackers, in particular, will create a sense of urgency in their messages to get victims to act quickly without thinking.
There are many phishing attacks which target victims, but the most common are spear phishing, whaling, domain spoofing, SMS phishing, clone phishing and vishing.
Spear phishing is a targeted phishing attack where the attacker has specific information about the victim, such as their name, job title, or company. This confidential information makes the message appear more legitimate and increases the chances that the victim will click on a malicious link or attachment.
Whaling is a spear-phishing attack targeting high-profile individuals within an organization, such as CEOs or CFOs. Vishing is a phishing attack that uses voice calls or VoIP instead of email.
The attacker will usually pretend to be from a legitimate organization and try to get the victim to disclose sensitive information or install malware on their system.
Some Examples Of Phishing
1. The Fake Invoice Scam: Attackers will send an email that appears to be from a legitimate company, often using the company’s logo and branding. The email will request that the recipient make a payment for an invoice and will provide instructions on how to do so.
However, the payment details will be for the attacker’s account. This scam can be difficult to spot, as the email will often look genuinely from the company in question. However, there are some red flags to watch out for, such as grammatical errors and inconsistencies in the branding. If you are unsure about an invoice, always contact the company to confirm before making any payments.
2. Email Account Upgrade Scam: In this scam, attackers will send an email claiming that your email account is about to be upgraded or migrated to a new server. The email will direct you to click on a link to confirm your account details.
Once you click on the link, you will be taken to a fake website that looks like the login page for your email provider. Entering your login information on this page will give the attacker access to your account. To avoid this scam, log in to your email account by typing in the URL. Do not click on any links in emails purporting to be from your email provider.
3. Job Offer Scam: In this scam, the attacker will send an email claiming to be from a recruitment agency or a potential employer. The email will often say that you have been shortlisted for a job and will ask you to click on a link to fill out an application form.
However, the link will take you to a fake website that steals your personal information. To avoid this scam, do not click on any links in unsolicited job offers. If you are interested in the job, research the company and contact them directly to inquire about open positions.
4. Lottery Scam: This scam typically comes in an email or letter claiming that you have won a large sum of money in a lottery. You will be asked to pay a fee or provide your personal information to collect your winnings.
However, there is no lottery, and you will not receive any money. Do not respond to unsolicited emails or letters claiming you have won a lottery to avoid this scam.
5. Charity Scam: This scam typically occurs after a natural disaster or another major event. Attackers will send emails or set up fake websites purporting to be from a legitimate charity.
They will ask for donations to help victims of the disaster. However, the money will go into the attacker’s account. To avoid this scam, do not click on any links in unsolicited emails or donate to charities you are unfamiliar with. If you want to contribute to a charity, research the organization first to ensure it is legitimate.

What is Pharming?
Pharming is a type of cyberattack in which hackers redirect traffic from a legitimate website to fraudulent websites that look identical to the original. The pharming scams aim to collect sensitive or confidential information, such as login credentials or financial data.
Pharming attacks can be challenging to detect, as they often do not involve any malicious code or phishing emails. Instead, hackers exploit vulnerabilities in DNS servers or redirect traffic using malicious JavaScript code.
As a result, users may inadvertently visit a fake site without realizing it. Pharming scams can have serious consequences if successful, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other types of cybercrime.
Pharming scams can be used to steal sensitive, confidential information like login credentials and financial information like bank account numbers. It can also install malware on victims’ computers or devices.
Pharming attacks can also occur when hackers insert malicious code onto a legitimate website. When users visit the site, their web browsers are redirected to the attacker’s site without their knowledge.
What About Countermeasures?
To protect against pharming attacks, keeping your computer and software up-to-date is vital. In addition, you should use a strong password and avoid clicking on links in emails or text messages from unknown senders.
Finally, you can install anti-phishing software that can help to block malicious websites and identify phishing emails. Taking these precautions can help protect yourself from this increasingly common type of cyberattack, thus protecting your confidential and personal information.
A Pharming attack is a severe cyber security threat because it is difficult to detect and can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations.
Victims of pharming often don’t realize that they have been redirected to a fake site until it’s too late, and by then, their personal information may have already been compromised.
There are several methods that attackers can use to launch a pharming attack:
- DNS hijacking – The attacker alters the DNS records for a legitimate website to redirect traffic to a fraudulent site.
- DNS Cache poisoning – The attacker exploits a vulnerability in the DNS software to insert false information into the cache, which is then used to redirect traffic from the victim’s browser.
- DNS spoofing – The attacker tricks the victim’s computer into thinking that the fraudulent site is a legitimate website.
- URL redirection – The attacker tricks the victim into visiting a fraudulent website by changing the link in an email or instant message.
- Man-in-the-middle attack – The attacker intercepts traffic between the victim and the legitimate website and redirects it to the fraudulent site.
- Social engineering – The attacker uses deception to trick the victim into visiting the fraudulent website.
- Trojan horse – The attacker installs a malicious program on the victim’s computer that redirects traffic to the fraudulent site.
- Botnet – The attacker uses a botnet to send large traffic volumes to the fraudulent site.
Some Examples Of Pharming
Cybercriminals often use pharming attacks to target financial institutions and e-commerce websites. In 2017, there was a major phishing attack against Experian, one of the largest credit reporting agencies in the world.
The attackers were able to redirect Experian’s website traffic to a fake site where they collected victims’ personal information. This information was then used to open new lines of credit in victims’ names and rack up huge amounts of debt.
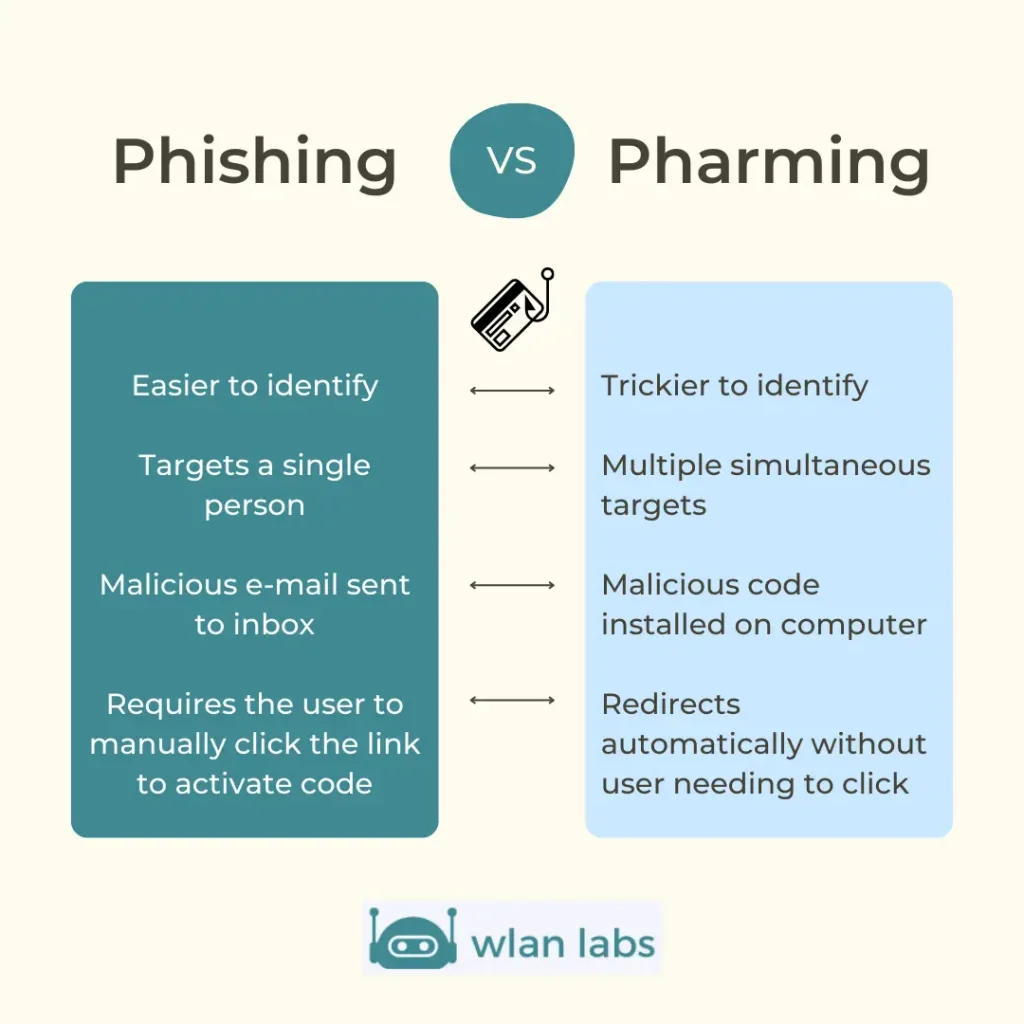
Difference between Phishing and Pharming
A phishing scam and pharming exploits are both attacks that seek to obtain sensitive information such as passwords or credit card numbers.
However, there are several key differences between these two types of attacks:
Phishing typically relies on social engineering techniques to trick users into revealing their credentials. For example, a phisher may send an email that appears to be from a legitimate company, instructing the recipient to click on a link and enter their login details.
Phishing attacks can also occur over the phone, where the caller pretends to be from a reputable organization and requests personal information.
In contrast, pharming does not require interaction from the user; instead, it uses malicious code to redirect victims to a fake website without their knowledge. Once on the fake website, victims may be prompted to enter their personal information, which the attackers will collect.
Another difference between phishing and pharming is that phishing attacks are often targeted, while pharming attacks tend to be more indiscriminate. That is, phishers will research their targets before launching an attack to maximize the chances of success.
Pharmers, on the other hand, typically do not target specific individuals or organizations; instead, they cast a wide net, hoping to trap as many victims as possible.
Finally, phishing attacks such as domain spoofing can be challenging to detect, as they often involve fake websites that look identical to the real ones.
Pharming attacks, on the other hand, are often more apparent, as they typically result in users being redirected to a website with a different URL than they were expecting. Scammers can then manipulate their victims into divulging bank details and other critical information.
While phishing and pharming attacks can be devastating, pharming is generally considered more serious due to its ease of execution and lack of need for user interaction. As such, it is important to be aware of the dangers of pharming and take steps to protect yourself from this type of attack.
What Are The Similarities Between Phishing and Pharming?
Phishing and pharming are both types of cyberattacks seeking to obtain victims’ sensitive information or data. They go to show security vulnerabilities and how easily they can be exploited.
Phishing and pharming can steal personal details such as login credentials, financial information, or other confidential data.
Both attacks typically use some form of social engineering to trick victims into revealing their information. For example, a phisher may send an email that appears to be from a legitimate organization, such as a bank or online retailer.
The email may contain a link that leads to a fake website that looks identical to the real site. The victim is then asked to enter their login credentials or other sensitive information on the fake site, which the attacker can use to access the victim’s account.
Similarly, a pharmer may create a fake website that appears to be the login page for a popular online service. When victims attempt to log in, they unwittingly provide their credentials to the attacker.
The Importance Of Security Awareness Training
The Importance Of Security Awareness Training can not be understated. With the current state of technology and the way that information is shared, it is more important than ever to be aware of the potential threats that exist.
Security Awareness Training helps to educate individuals on the risks that are associated with the use of technology. It also guides how to protect user’s credentials and themselves from these risks.
Cybersecurity awareness training can help to prevent data breaches and other security incidents. Security Awareness Training can also help reduce the impact of a security incident, should one occur. The importance of training is evident, and businesses, and individuals alike, would be wise to invest in it.
How can you stay safe from Phishing and Pharming?
Here are some tips:
- Don’t click on links in emails, even if they look legitimate. If you’re unsure, go to the company’s website and find the information you’re looking for.
- Be suspicious of emails that ask you to provide personal information, even if they look from a legitimate company. Call the company or log into your account on their website to verify the request if you’re unsure.
- Don’t enter personal information on websites that you’re not familiar with. If you’re unsure if a website is legitimate, search for the company or website name to see if there are any warnings about it.
- Keep your antivirus and anti-malware software up to date, and run regular scans of your computer. This will help protect your computer from any malicious software that might try to install itself.
- Consider implementing phishing testing solutions if you have a business with a reasonable number of employees. Testing for phishing vulnerabilities is important because if just one person falls for a phish, it can jeopardize an entire company.
- Phishing is becoming increasingly sophisticated, so organizations need to be proactive in their defenses. Phishing tests can help identify weaknesses in an organization’s security posture and educate employees about recognising and avoiding phishing attacks.
What is the difference between phishing and pharming? Conclusion:
As you can see, phishing and pharming are two very different things. Both pose serious dangers to the cyber realm. Despite their distinct features and distinctions, they’re designed to steal private information.
In simple terms, pharming involves the attempt to install malicious software on the online users device, which redirects them to a fraudulent website.
Phishing is the practice of sending persuasive emails to entice users to obtain their personal information. It seeks to exploit software or security vulnerabilities and make illicit financial gains.


